I have to focus a lot on ethical leadership in my job as a CEO. Otherwise, people would not follow me. If I lack ethics, people will not trust me, and therefore they will not believe in my visionary leadership, my communication, or anything else of what I do. Ethical leadership should be a cornerstone for every leader since it is the basics for general trust.
What is Ethical Leadership?
Ethical leadership means a strong focus on morale, values, and doing the right thing, even when costly or complicated. Ethical leaders create accountability while reducing the risk of costly errors and wrong-doing, although it can result in some bureaucracy.
Contents
- What is Ethical Leadership?
- What Are the Four Elements of Ethical Leadership?
- What are the Pros and Cons of Ethical Leadership?
- How Can You Be an Effective Ethical Leader?
- Ethical Leadership Examples
- Ethical leadership: a career example of an unethical leader
- Ethical Leadership Links, Articles, References
What is Ethical Leadership?
Business ethics is often considered a grey area. According to David De Cremer[i] from the London Business School,
“Ethics is not easy to define – let alone comply with. Two popular business observations are that:
- It’s okay to push the limits but not cross the boundaries of the law.
- Ethics is about grey zones, so it’s hard to take responsibility.”
Ethical leadership arose out of a need to clarify the grey area of business ethics. The Enron Corporation scandal is a prime example of the need for ethical leadership amidst business ethics’ grey zones. Enron’s mark-to-market accounting[ii] practices, although inherently legal, allowed them to report inflated profits and hide monumental losses. Their unethical practices ultimately led to the company’s bankruptcy and a $74 billion loss for shareholders.
It’s fair to assume that ethical leadership should be a natural part of all leadership. However, this isn’t always the case. Let’s look more closely at what ethical leadership is and how to use it effectively.
Why is ethical leadership important?
Ethical leadership is essential since it establishes basic trust, morale, and rules in a team, with the ethical leader setting a clear example for others to follow. Once implemented, basic ethics serve as a platform for decisions, how people treat each other and how the organization does business.
Ethics and integrity are often used interchangeably. They are similar terms, but integrity is more intrinsic, while ethics is an outward manifestation of moral principles. Oprah Winfrey once said that “real integrity is doing the right thing, knowing that nobody’s going to know whether you do it or not.” Ethical leaders are expected to have integrity. They are identified as ethical leaders because they follow the organization’s rules and regulations that align with moral principles. Ethical leadership is a leadership framework rather than a leadership style. This means you can use various leadership styles while also being an ethical leader at the same time.
Michael E. Brown and Linda K. Treviño provided an even more precise definition in their study[iii] on the similarities and differences between ethical leadership and other leadership styles. They define ethical leaders as those who “explicitly focus attention on ethical standards through communication and accountability processes.” Therefore, communication and accountability are essential features of ethical leadership.
It is believed that ethical leadership is based on the decision-making strategies of three separate leadership theories.
| Theory | Basic Concept | Creator |
| Utilitarianism | Followers must feel good before choosing one action over another. | John Stuart Mill |
| Libertarianism | The freedom of the follower should be protected. Any decision that threatens this freedom should be rejected. | Aristotle |
| Ethical | The leader must follow the rules and customs of the organization so that moral and ethical actions can be carried out. These common, agreed values help the leader make the right decision. | Immanuel Kant |
What Are the Four Elements of Ethical Leadership?
Bill Grace is credited with developing the 4-V Model of Ethical Leadership. He is one of the founders of the Center for Ethical Leadership and believes that an ethical leader can only function effectively through understanding his or her core values and how they fit in with the organization’s overall vision. Only then can this vision be something that inspires followers.
The four V’s represent values, vision, voice, and virtue and are aptly depicted in the diagram below.
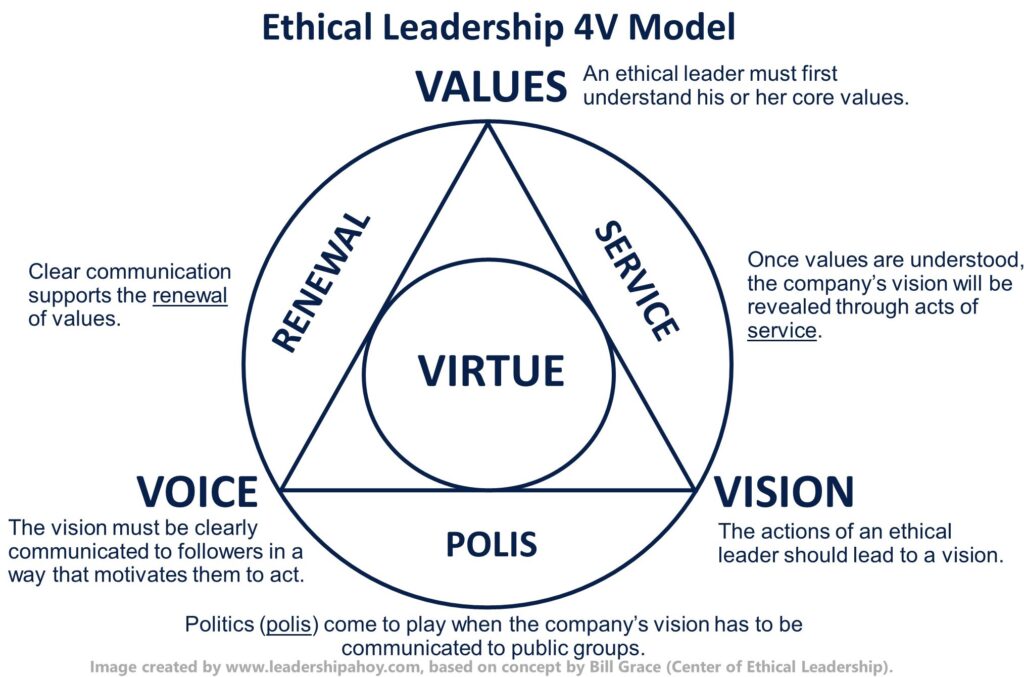
| The Four Elements of Ethical Leadership | Description |
| Virtue | This is the core of the 4-V model. Ethical leaders exhibit virtuous behavior and act as role models for those they lead. |
| Values | An ethical leader must first understand his or her core values. |
| Vision | The actions of an ethical leader should lead to a vision. |
| Voice | The vision must be clearly communicated to followers in a way that motivates them to act. |
As depicted in the diagram, the 4 V’s are connected by three additional elements: service, polis, and renewal. Once values are understood, the company’s vision will be revealed through acts of service. Politics (polis) come to play when the company’s vision has to be communicated to public groups. Clear communication supports the renewal of values. If both don’t coincide, the leader doesn’t act.
What are the Pros and Cons of Ethical Leadership?
These are the advantages and disadvantages of ethical leadership, and learning those helps you to better master the art of ethical leadership.
Advantages of Ethical Leadership
The advantages of ethical leadership are:
1. There is a great sense of accountability.
Ethical leaders believe that everyone, including the leaders, should be held accountable for their actions. Therefore, the leader implements high standards across the board to ensure that ethics and high quality are maintained.
2. Decision-making also considers the impact on the team.
Decision-making isn’t only a matter of what’s right or wrong. An ethical leader also considers how decisions will impact the team. Yes, the right decision that aligns with the leader’s values will prevail, but the leader will also consider any impact on the people involved to minimize harm as much as possible. (This is also a cornerstone of Affiliative Leadership.)
3. There is an emphasis on communication and collaboration.
Ethical leaders encourage followers to express their opinions. There is mutual respect between these leaders and their followers. Ultimately, this leads to a positive work environment where workers feel valued. (This is similar to democratic leadership and transformational leadership.)
4. It minimizes the risk of costly errors.
Followers are more likely to report problems, no matter how small, to an ethical leader. This helps the leader get a headstart on issues within the organization before they blossom into something huge. Over time, this improves the organization’s bottom line.
5. Consistency is a norm.
There is no room for doubt in ethical leadership. Followers expect ethical leaders to operate within their values and vision consistently. In fact, these leaders always strive to exceed the expectations placed on them.
Disadvantages of Ethical Leadership
The disadvantages of Ethical Leadership are:
1. The leader must be influential.
The tenets of ethical leadership assume that the leader can influence followers to hold true ethics and the company’s vision. Everyone needs to be on board, especially C-Suite executives who head the organization. Some leaders may not have such widespread influence and may also not have the charisma required to accomplish this goal. (Learn more about influence in our article about Charismatic Leadership, a leadership style that sadly can be misused.)
2. It’s easy to forget that the leader can make mistakes.
There are high expectations on an ethical leader. The fixation on these expectations often leads to people overlooking the leader’s mistakes or problems. The thought in people’s heads is that an ethical leader would never do that (whatever “that” is)awful thing.
3. Maintaining highly ethical standards can affect a company’s bottom line in the short term.
An organization may view an ethical leader as a liability because upholding ethics sometimes runs contrary to maintaining short-term profits. For instance, the costs of keeping regulations can impact an organization’s bottom line. The effect, however, does balance out in the long term.
4. Ethics can have multiple definitions.
Ethics can mean different things to different people because it depends on what each individual believes is morally correct. Everyone in the organization needs to be clear about the moral compass that guides the ethical leader so that everyone is on the same page.
How Can You Be an Effective Ethical Leader?
Now that you know and understand the concept of Ethical Leadership and its benefits and weaknesses, it’s time to consider how to implement it in your organization best.
Become a more effective ethical leader by using the following steps:
1. Ensure that your team supports the organization’s values.
You should know the organization’s values and be able to communicate them to your team effectively. It doesn’t stop at communication, though; you should lead by example because your team closely observes what you do. Consistently model what ethical behavior looks like, and your team will follow. Apply several methods of communication as described in our article on 17 tips to Improve Leadership Communication.
2. Rewards and consequences should be clear.
Followers should be rewarded for consistently upholding the company’s values. A reward could be as simple as a compliment or a thank you card, anything that shows that you appreciate them staying on the right path. On the flip side, there should be consequences that relate to failing to uphold the company’s values. Rewards and consequences should be clearly communicated so that the team knows what to expect. You can gain inspiration from this approach to rewards in leadership: Transactional Leadership.
3. Work with an organization that has values that align with your values.
Ethical leaders follow their personal values and the organization’s values. This is difficult if your personal values and the organization’s values are misaligned. This is especially true when people within the organization are doing unethical activities because they aren’t illegal. Step away from the organization if this is happening. You can learn a lot about how you as a leader affect values and culture by reading our article here: How do leaders affect organizational culture?
Ethical Leadership Examples
Here are three examples of ethical leaders:
James Burke – Former CEO of Johnson and Johnson – (Born 1925- Died 2012)
James Burke was named one of the greatest CEOs of all time by Fortune magazine[iv]. He was praised for his ethical leadership style throughout his time as leader of Johnson and Johnson. His leadership style became particularly evident when Johnson and Johnson faced a Tylenol crisis in 1982.
Tylenol was the company’s best-selling product at the time. Therefore, Burke had to act swiftly when seven people in Chicago died in 1982 after taking cyanide-laced capsules of Extra-Strength Tylenol. He recalled all Tylenol products despite the financial loss. He even allowed the media to film company meetings where solutions for this challenge were discussed, and he also appeared on television introducing new steps the company would take to protect its products. The company absorbed all the costs of these activities rather than passing on the costs to the consumer.
Tony Hsieh – CEO of Zappos – Born 1973
Hsieh has an unconventional and passionate approach to company culture. His approach has helped him create a culture at Zappos that landed the company on Fortune magazine’s 100 Best Companies to Work For list in 2014[v]. A lot of this success can be attributed to his ability to make ethics a part of Zappos’ core values. He expects alignment between the organization’s values and vision.
Howard Schultz – Former CEO of Starbucks Coffee – Born 1953
Starbucks has consistently been named one of the World’s Most Ethical Companies by Ethisphere[vi]. Howard Schultz was one of the company’s pioneering leaders who helped contribute to this status. All employees (part-time and full-time) receive healthcare, and there is great emphasis on the employees’ happiness.
The company’s coffee is ethically sourced. Additionally, one of the requirements for a business partnership with Starbucks is that the business partner’s core values align with those of Starbucks.
Ethical leadership: a career example of an unethical leader
I once worked for a leader who expected ethical behavior of everyone else, despite displaying an apparent lack of ethics on his own. Every time he breached basic morals and ethics, he lost credibility, influence, and authority in the organization. In the end, people avoided him as much as possible. This leader was an autocratic leader, despite his belief that he was approachable, trustworthy, involving, and pleasant.
Here are some examples of unethical behavior he displayed:
- Paying for personal expenses with company money
- Lying and manipulating people
- Bullying selected individuals
- Trying to find out who responded unfavorably to anonymous surveys
These behaviors led to the following reactions in his team and his surroundings:
- Less transparency: don’t be the messenger, especially for bad news
- No one wanted to provide honest feedback
- Few people wanted to go the extra mile for the company
- Avoid taking the initiative since you risk punishment if you make a mistake
- Mind your own business to avoid risk. This led to poor cooperation in the team.
- Several of the key people left the organization
- Unethical behavior with shortcutting rules, personal expenses, etc. (It is obviously acceptable since the leader does it.)
This leader eventually left the company, to the great relief of everyone still in the organization.
Ethical Leadership Links, Articles, References
https://www.villanovau.com/resources/leadership/what-is-ethical-leadership/
https://www.mindtools.com/pages/article/newLDR_58.htm
https://www.cleverism.com/ethical-leadership-guide-definition-qualities-pros-cons-examples/
https://futureofworking.com/14-advantages-and-disadvantages-of-ethical-leadership-styles/
[i] https://www.london.edu/think/business-ethics-black-white-or-grey
[ii] https://www.investopedia.com/updates/enron-scandal-summary/
[iii] https://www.nipc.ir/uploads/science_p_10105_5765.pdf
[iv] https://money.cnn.com/magazines/fortune/fortune_archive/2003/07/21/346095/index.htm
[v] https://www.zappos.com/about/stories/zappos-makes-fortune-100-best-companies-to-work-for-list
[vi] https://stories.starbucks.com/stories/2018/starbucks-worlds-most-ethical-companies-2018/




