We have more than 27 leadership styles in this huge leadership styles database containing more than sixty leadership style articles. This complete guide to Leadership Styles focuses on you and your possibility of learning which leadership styles to use and which to avoid. Each leadership styles framework has an overview article, with further deep dive into each leadership style.
What is a leadership style?
A leadership style is a process by which a leader seeks the participation of followers to reach their goals. A leadership style’s effectiveness depends on the involved people, the leader’s skills, and situational circumstances. Great leaders adapt to the circumstances and use multiple leadership styles.
The various leadership styles are presented in the clusters they belong to in terms of leadership theories, just click on the links or images to go to an in-depth article on that leadership styles. You can also read about the evolution of leadership styles further down on this page or take our Lewin leadership styles test to find out more about yourself.
Every leadership styles article include explanations, pros and cons, how, why, and when to use, and real-life leadership style examples from my job as a CEO of a global company. If you just want a long list of summarized leadership styles, scroll down for 25+ styles with brief explanations. Please share the link to this site with friends and colleagues so that others can benefit from these leadership styles articles as well.
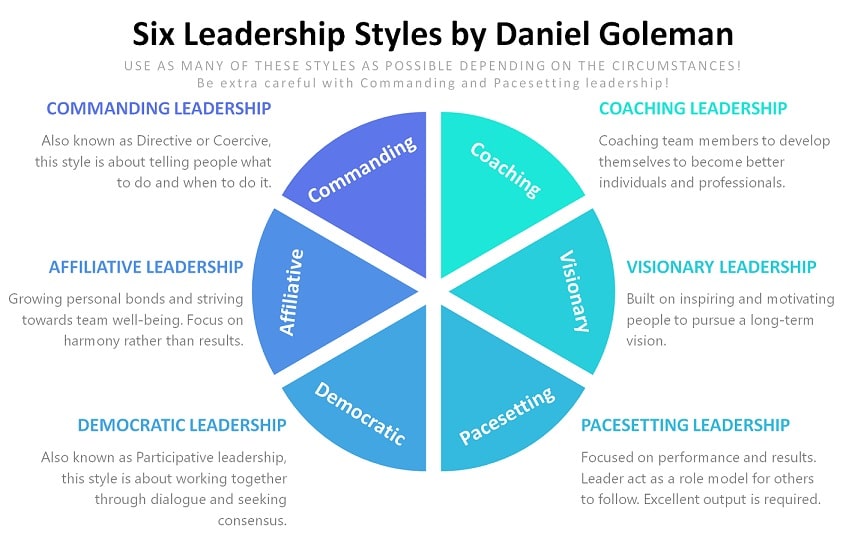
The Six Leadership Styles by Goleman
Resonant leadership is when a leader creates a positive organizational climate where engagement and performance are high by using Emotional Intelligence and the Six Leadership Styles by Goleman. Successful implementation of resonant leadership in a team results in comfort, cooperation, idea sharing, and strong bonds, by using the visionary leadership, pacesetting leadership, democratic leadership, commanding leadership, affiliative leadership, and coaching leadership styles. (Join our newsletter and get some of my secret tips for each of the Goleman leadership styles.) Ultimately, this drives team performance, as scientifically proven. (I use these myself in my CEO role. I have packed some secret tips in this democratic leadership course as well.)
Democratic Leadership
Also known as participative leadership, democratic leadership is about collaboration through dialogue and seeking consensus, which leads to engagement and innovation.
Affiliative Leadership
Affiliative leadership grows personal bonds and strives toward team well-being. This leadership styles puts much stronger focus on harmony than on results.
Pacesetting Leadership
Focused on performance and results, pacesetting leadership means acting as a role model and setting excellent standards for others to follow.
Commanding Leadership
Also known as directive or coercive, commanding leadership is about telling people what to do and when. Commanding leaders provide rules, instructions, and clarity.
Coaching Leadership
Coaching leadership emphasizes the development of employees. Through support, mentoring and assistance, each team member is developed into a better person.
Visionary Leadership
Built on inspiring and motivating people, visionary leadership creates unity in pursuit of a long-term common goal, building engagement and performance.
The Full Range Leadership Model
The Full Range Leadership Model (FRLM) framework is designed as a linear approach to leadership styles, starting with crude tools and developing into precise and effective leadership instruments. In the proper nomenclature of the FRLM, a leader's worst option is laissez-faire leadership, followed by three levels of transactional leadership, and ending with four elements of transformational leadership.
The Laissez-Faire
Leadership Style
Laissez-faire leadership is virtually zero leadership in FRLM. The leader leaves people on their own, with some remaining focus on providing them resources.
The Transactional
Leadership Style
Transactional leadership is built on clear rules and structures where the leader and the employee enter a pre-defined exchange of performance for rewards.
The Transformational
Leadership Style
The motivational and inspirational transformational leadership builds great employee engagement and strives toward an over-arching goal.
Lewin's Leadership Styles
The Kurt Lewin leadership styles toolbox from the 1930s is behavioral, i.e., every leader has one of three personalities or behaviors. This framework excludes situational dependency, making it dated compared to the Goleman Leadership Styles and the FRLM. The Lewin leadership styles, autocratic, democratic, and laissez-faire, are frequently mentioned but do not fit for modern leaders. I even wrote a book about this framework, you can find it here: Leadership Styles Classics: Autocratic, Democratic and Laissez-Faire (Amazon).
The Autocratic
Leadership Style
Autocratic Leadership involves the leader making all decisions single-handedly, rarely seeking advice or input from others.
The Democratic
Leadership Style
In Democratic Leadership, the leader and the team make decisions together, although the leader has the final say.
The Laissez-Faire
Leadership Style
Laissez-Faire leadership means that the followers make all the decisions on their own, also known as "zero leadership".
Max Weber's Leadership Model
Max Weber's three “ideal types of legitimate domination”, bureaucratic, charismatic, and traditional leadership, originated in the 1920s. Each type of domination was a leadership style based on enough legitimacy for the followers to accept being led.
Collection of Other Leadership Styles Theories
The Situational Leadership
Model
The Situational Leadership Model builds on group maturity, four situation types, and two leadership behaviors, resulting in a very concrete leadership model with telling, selling, participating, and delegating leadership styles.
The Servant Leadership Approach
Servant Leadership focuses on improving people, society, and organizations. Servant leaders serve others, which leads to strong ethics, and engaged, motivated employees. If gone too far, organizational goals and purpose might become secondary.
The Great Man Theory
The Great Man Theory of Leadership from the 1840s states that leaders are born with certain traits, making them great men destined for leadership. Great Man Theory is unscientific and does not belong in modern leadership.
The Michigan University Studies
The Michigan Leadership studies were undertaken in the 1950s and concluded that leaders could be job-oriented, with a focus on production, or employee-oriented, with a focus on people.
Blake and Mouton's
Managerial Grid
The Blake and Mouton Managerial Grid was developed in the 1960s and enables leaders to use a visual aid to quickly assess which leadership style they use, depending on their levels people vs production two behaviors.
Contingency Leadership Theory
The Contingency Theory of Leadership collects all the situational approaches to leadership behaviors and styles. Ever since it came in the 1960s, it has been dominating most leadership discussions. Includes Fiedler's Model, Path-Goal, and many others.
Path-Goal
Theory
Path-Goal Theory is a leadership approach where the leader clearly identifies goals and the path to reach them. The leader uses four leadership behaviors, depending on employee and environmental factors.
The Ohio State Leadership Studies
The Ohio State Leadership Studies showed that leadership performance depends on two behaviors: Initiating Structure and Consideration. It also concluded that leaders aren't born, but can be made.
The Spiritual Leadership
Style
The Spiritual Leadership style goes beyond performance targets and saving the bottom line. It adds focus on altruistic love, people, faith, and the planet. and helps leaders appreciate that people want meaningful work.
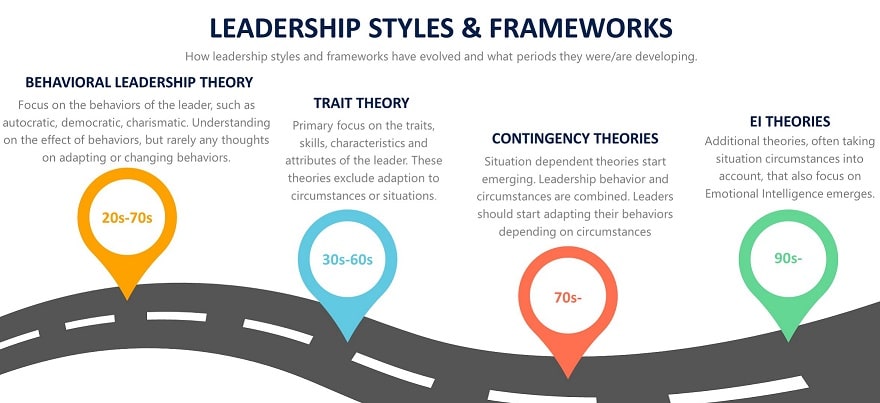
Behavioral Leadership Theory
Although a bit older, the behavioral leadership theory family of leadership approaches can still teach us plenty on our behaviors and their impact. Includes Blake & Mouton, Ohio State, Michigan University, and several other leadership theories and styles.
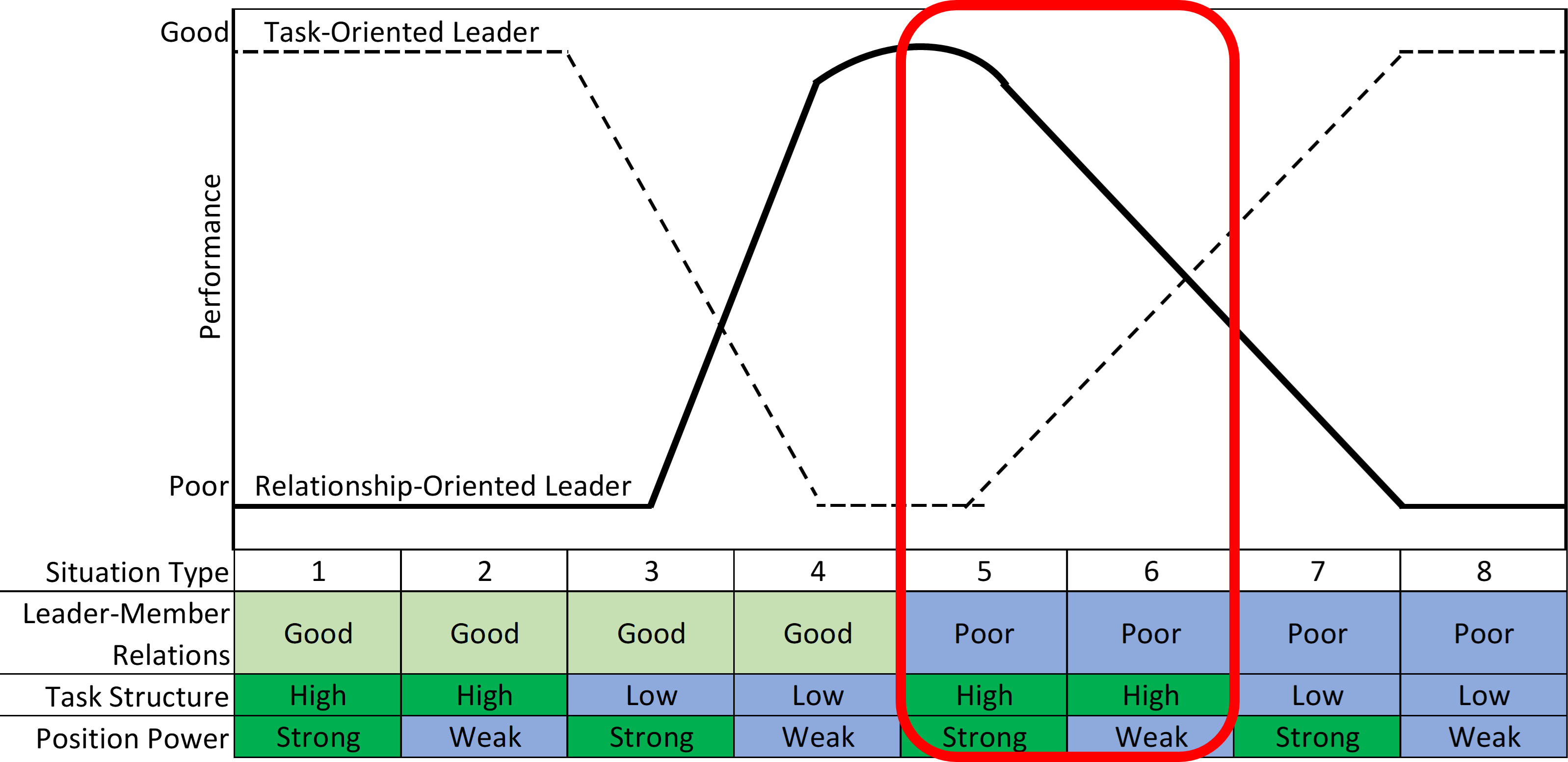
Fiedler's Contingency Model
Fiedler’s contingency model of leadership explains which type of leader leads to high performance in one of eight different situations, depending on three dimensions, all described graphically.
Leadership Styles Video Collection
We have created numerous leadership styles videos on our Leadershipahoy Youtube channel. Examples include the six leadership styles by Goleman, Servant Leaership, Lewin leadership styles, and many others.
Leadership styles – History and Development
An organization needs leadership to operate, develop further, grow, and ultimately achieve its goals. There are plenty of leadership styles available, some old, and some modern. The approach to leadership styles and how to use them has changed over the years, which we will briefly explain in this chapter. Beyond this introduction, the 25 leadership styles mentioned above will be presented in brief, together with a few comments on the useability of each style based on my experience as a CEO.
History of Leadership Styles
- Max Weber’s Classification of Authority from the 1920s listed three ways a leader could gain authority, which to some extent can be seen as leadership styles. These styles are charismatic leadership, bureaucratic leadership (rational-legal leadership), and traditional leadership.
- The trait theory of leadership, popular in the 1940-60s, focuses on the skills, characteristics, and attributes of the leader as a person. This did not involve any leadership styles, since it was all about the traits of the leader.
- Behavioral leadership theories focus on ideal leadership behaviors, regardless of situational circumstances. These concepts started emerging in the 1930s, and the Kurt Lewin leadership styles are the most known example of this. Most of these behavioral models are built on every leader having his or her personal style, i.e., the style was not an active choice by the leader. (The Ohio State Leadership Studies and the Michigan Leadership studies are two other behavioral leadership frameworks.)
- Contingency models and situational leadership styles have since the 60s been adding the perspective of situational factors to leadership. This means that traits, behaviors, and the situation at hand affect which leadership style the leader should choose to get specific results. (The six leadership styles by Goleman are examples of this approach.)
Feel free to use this image, as long as you link back to this page.
Leadership Styles - The Complete List
The 25 leadership styles are grouped in connection with the framework they belong to. However, there are a few exceptions to this regarding leadership styles that belong to several frameworks.
The first six leadership styles belong to the Goleman framework of Resonant leadership based on Emotional Intelligence.
1. Pacesetting Leadership Style
I think many business leaders, including myself, lean toward pacesetting. This is because Pacesetting leadership creates visible results quickly. Achieving results fast can lead to early promotion, resulting in pacesetting leaders moving up in the hierarchy.
What is the Pacesetting Leadership Style?
Pacesetting leadership is when the leader sets an example of high performance, pace, and quality. Team members are expected to follow suit, and the pacesetting leader values results the most. Pacesetting leadership is good for reaching short-term targets but is detrimental to long-term employee engagement.
The pacesetting leadership style is one of the six leadership styles in the Daniel Goleman model of 2000. It has a very strong task orientation, with a low focus on people, since it is all about getting the job done. Pacesetting is very different from commanding or autocratic leadership since it is about setting a high-performing example for others to follow, rather than ordering people around expecting immediate obedience. The Pacesetting leadership style is similar to the Achievement-Oriented leadership style, which belongs to House’s Path-Goal theory.
Advantages of the Pacesetting Leadership Style:
- It can substantially increase performance for a limited time
- Short bursts of increased performance build team confidence and commitment, as long as it is not too often
Disadvantages of the Pacesetting Leadership Style:
- Overuse leads to stressed team members with low engagement
- The focus on performance leads to a poor level of people focus, meaning a lack of coaching and development of individuals
I teach you exactly how to paceset at the right level which gets results without overly stressing your team through simple techniques in my Pacesetting Leadership Blueprint. You can also read more about this style in our in-depth article on the Pacesetting Leadership style.
2. Democratic Leadership Style
We have reached one of the most popular, engaging, and effective leadership styles. If you consider yourself a leader, you must learn and master the democratic leadership style to a level where you can enjoy its advantages while limiting and controlling its disadvantages. Sadly, a lot of autocratic leaders are unlikely to be open-minded enough to make it work. If you are serious about taking your leadership to the next level and boost your career, check out the democratic leadership course I have created for you, it is loaded with tips and tricks that I use in my job as a CEO.
What is the Democratic Leadership Style?
Democratic leadership builds on empowering team members to participate in decision-making, with a strive toward consensus. The engaging climate welcomes everyone’s opinions, leading to robust solutions. However, the democratic leader still has the final say on any decisions. This style is sometimes slow but generally very effective.
The Democratic Leadership style was introduced in the 1930s as one of the three leadership behaviors used in the Kurt Lewin experiments in 1938. The Lewin model assumes a leader has one of the three behaviors, and there is no push for leaders switching styles depending on circumstances. (Laissez-faire and autocratic leadership were the other two in the Lewin model.)
Democratic leadership is also included in the modern framework based on Emotional Intelligence, also referred to as the Goleman leadership styles. The Goleman version is defined as a situational style to be used with five other styles. The democratic leadership style is also called participative leadership, and it resembles the Team Leadership Style from the Blake and Mouton Managerial Grid and the participative leadership style of the Situational Leadership Model even more. Last but not least, the participative leadership style of House’s Path-Goal theory is very similar to the democratic leadership style as well.
Advantages of the Democratic Leadership Style:
- Creativity and innovation are encouraged
- Collaboration creates solid solutions for complex problems
- Employee engagement is high
- Common goals lead to high accountability
Disadvantages of the Democratic Leadership Style:
- Collaborative decision-making is time-consuming
- Productivity can temporarily decline when awaiting decisions
- It does not work well in low skilled, inexperienced teams
Democratic leadership can be truly powerful, and I have personally used it to transform companies with more than a thousand employees. It can be tricky to balance though, and you must get the optimum level of collaboration without going too far as results might suffer. I teach you exactly how to do this in my democratic leadership master course. If you learn those advanced techniques, I am sure will unlock additional creativity, engagement, motivation and performance, likely also giving you a career boost as well. You can also learn more basic information in our article here on the Democratic Leadership style.
3. Affiliative Leadership Style
A good leader knows to care about the team members and is not afraid to show it. A confident and strong leader is also ok with sharing feelings and thoughts with others without considering it a display of weakness. A leader who desires an open and trusting dialogue needs to start by being honest and setting the stage for that dialogue.
What is the Affiliative Leadership Style?
Affiliative leadership is completely focused on the people and relationships in an organization. The leader’s primary task is to ensure harmony and friendship in the workplace. This leads to happy employees but can at the same time lead to poor performance.
The Affiliative Leadership Style is one of the six leadership styles by Goleman, which are based on Emotional Intelligence. Overly focusing on Affiliative Leadership compares well to Country Club Leadership, which is worth avoiding. However, the most striking similarities are probably compared to the supportive leadership style of the Path-Goal theory, which focused on employee well-being, reduction of stress, social satisfaction, etc.
Advantages of the Affiliative Leadership Style:
- The team feels that the leader genuinely cares about them, which builds loyalty, commitment, and trust
- Positive communication and strong people focus
- Strong bonds between members help in collaboration and crisis handling
Disadvantages of the Affiliative Leadership Style:
- Underperformance might be accepted (Country Club Leadership)
- The focus on harmony can result in avoidance of conflict and critical feedback
- The overall goal might be lost, and the strive for harmony takes over
Read more in our in-depth article on this style here: the Affiliative Leadership style.
4. Coaching Leadership Style
Why would coaching be restricted to the world of sports? All leaders who desire performance should spend some time developing their team members, and the coaching leadership style is perfect for that.
What is the Coaching Leadership Style?
Coaching leadership focuses on improving employees to become better individuals and professionals with the leader as a coach. A Coaching leader can sacrifice initial performance for learning opportunities. Coaching leadership is very effective in the long term but can be difficult and time-consuming.
Coaching Leadership was coined by Daniel Goleman in 2000 and is part of his six leadership styles based on emotional intelligence. There are streaks of coaching leadership within the transformational leadership style, but besides that, it is rather unique among leadership styles.
Advantages of the Coaching Leadership Style:
- It leads to high engagement and low turnover within the team
- It develops people to perform more and better in the future
- Coaching builds empowerment and confidence in people
Disadvantages of the Coaching Leadership Style:
- Coaching is difficult and time-consuming
- Coaching requires commitment from both parties
Improve your leadership by learning more in our article on the coaching leadership style.
5. Visionary Leadership Style
The Visionary leadership style is one of the best leadership styles available today. I incorporate Visionary leadership in my job as a CEO as often as I can.
What is the Visionary Leadership Style?
Visionary Leadership is when a leader inspires others to pursue through the use of a long-term vision. The Visionary Leadership style builds on participation, communication, and goal setting. A visionary leader risks tunnel vision and losing short-term focus since all efforts are focused on the long-term results.
The Visionary Leadership style is also known as the authoritative leadership style and is one of the six leadership styles introduced by Daniel Goleman in 2000. It has substantial similarities with transformational leadership and some similarities with charismatic and servant leadership. Furthermore, visionary leadership was found to have the most substantial positive impact on organizational climate in Goleman’s research.
Advantages of the Visionary Leadership Style:
- A clear vision creates motivation, inspiration, and unity among team members
- Innovation and creativity thrive under visionary leadership
- Strong awareness of change drivers in the surrounding world increases the chance of successful adaption by the organization
Disadvantages of the Visionary Leadership Style:
- The strong emphasis on the long-term can lead to overlooking short-term and operational matters
- If the vision becomes too intertwined with the personality of the leader, it can turn into charismatic leadership, which has substantial adverse effects
Take the opportunity to learn more about this great style in our article available here: the Visionary Leadership style.
6. Commanding Leadership Style
Sometimes, and I want to underline the word sometimes, a leader needs to be decisive and take fast decisions that even go against the will of the team members. That is where commanding leadership should be used. Commanding leadership can have the same advantages as the autocratic style but without the disadvantages, if applied right.
What is the Commanding Leadership Style?
A commanding leader makes all the decisions and gives orders to his or her team. Tight control and follow-up combined with high clarity in rules, roles, and expectations are key elements of Commanding leadership. This style can be efficient in low-skilled teams and when decisions must be made very quickly. This style can lead to micromanagement, which is detrimental to employee engagement, especially in highly skilled teams in complex environments.
The commanding leadership style was presented as one of the six leadership styles by Daniel Goleman back in 2000 and is also known as coercive or directive leadership. This style is similar to autocratic leadership but with a foundational difference: it is meant to be applied rarely and in a controlled fashion, whereas autocratic leadership is more of a permanent state and behavior. There are relatively many similarities with the telling leadership style from the Situational Leadership model, although the long-term intent is different. Houses Path-Goal Theory from 1971 also contains a directive leadership style.
Advantages of the Commanding Leadership Style:
- Increased clarity on roles, expectations, and rules, beneficial for low skill teams
- Confidence and decisiveness, especially useful in times of crisis
Disadvantages of the Commanding Leadership Style:
- High dependency on the leader, who also need to know how to perform all jobs and tasks in detail
- Morale, motivation, and engagement are low, and work climates can become toxic
- Creativity and participation is minimal
Learn more in our detailed article on the directive/commanding leadership style. (Join our newsletter and get some of my secret tips for each of the Goleman leadership styles.)
7. Servant Leadership Style
The well-known Servant leadership style sticks out from the rest of the styles in this list. Despite being relatively modern, it does not build on a situational approach involving the switching between leadership styles, but instead stays with a strict focus on servant leadership in a framework separate from all others.
What is the Servant Leadership Style?
Servant Leadership focuses on improving people, society, and organizations. In Servant Leadership, the leader serves others, which leads to strong ethics, and engaged, motivated employees. However, a Servant leader with too much focus on serving others can lose track of organizational goals and purpose.
The Servant leadership style was first defined in 1970 by Robert K. Greenleaf in an essay where he outlined that there were two types of leaders: Servant-First and Leader-First. The first type focuses on the success of others, and the second type cares more about themselves and their personal success. Servant leadership stands out and is difficult to compare with the other styles, but transformational leadership comes the closest in my mind.
Advantages of the Servant Leadership Style:
- Participation and a common cause leads to high engagement
- Strong ethical behavior
Disadvantages of the Servant Leadership Style:
- It does not work for all companies and organizations since an overarching cause is at the core of servant leadership
- True servant leaders are challenging to find since they need to have a complete lack of ego
- Business and organizational goals might be lost in the struggle for the long-term cause
Read more about this style in our article on the Servant Leadership style here.
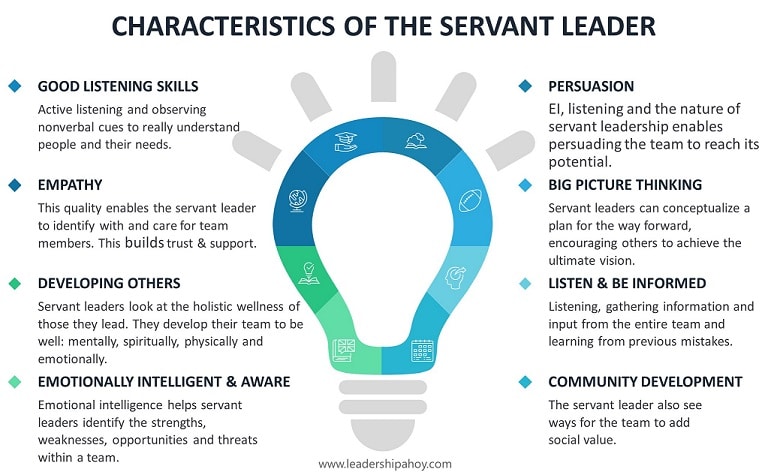
Feel free to use the Servant Leader Image as long as you link back to this page.
The upcoming Transformational and Transactional leadership styles are part of the Full Range Leadership Development framework together with the Laissez-Faire leadership style. Sprung out of the late 70s, this framework has been developed additionally since then.
8. Transformational Leadership Style
Transformational leadership is one of the most well-known and popular leadership styles available, and many articles have been written on the subject.
What is the Transformational Leadership Style?
Transformational leadership creates substantial change for team members as well as organizations. Expectations, aspirations, perceptions, and values are transformed into something better. Transformational leadership develops the team members and motivates and inspires them to reach extraordinary success.
Transformational leadership was first defined by James MacGregor Burns in the late 70s as part of Full Range Leadership. Bass and Avolio developed transformational leadership and the Full Range Leadership Model further in subsequent years. The transformational leadership style compares well to a combination of democratic, visionary, and coaching leadership among the six leadership styles by Goleman. Transformational leadership also has some commonalities with Servant leadership.
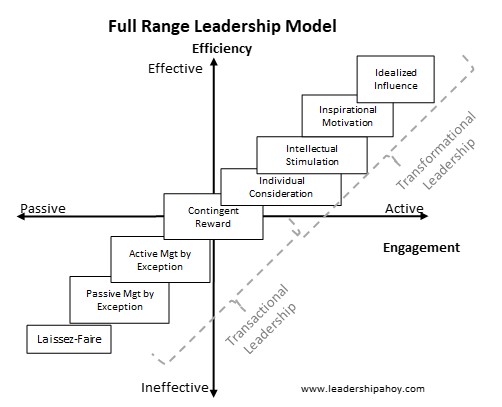
Feel free to use the image, as long as you link back to this web page.
Advantages of the Transformational Leadership Style:
- It is excellent for change management and growth
- High transparency and strong communication builds participation and engagement
- The shared vision results in inspiration, motivation, and collaboration
Disadvantages of the Transformational Leadership Style:
- Transformational leadership can be very time consuming and long term
- It does not work well without a strong change element or vision
- Can result in too much risk-taking and overlooking short-term requirements
Want to know more? Read our article on the transformational leadership style.
9. Transactional Leadership Style
Transactional leadership can be seen as the more autocratic and less visionary sibling of transformational leadership, refer to the overview image above in the area about transformational leadership.
What is the Transactional Leadership Style?
Transactional leadership is built on a clear structure of reward and punishment for different levels of performance. It is focused on results, efficiency, and performance rather than people and relationships. Transactional leadership is often seen as the opposite of transformational leadership.
Transactional leadership is an expansion of the bureaucratic leadership style and it was conceptualized by Burns together with the transformational leadership style. The two styles were seen as mutually exclusive, until Bass and Avolio developed the model further, adding that a leader can use both styles as appropriate while also adding Laissez-Faire to the mix of the Full Range Leadership Model.
Advantages of the Transactional Leadership Style:
- There is a clear connection between performance and rewards
- It can be very productive, especially when it comes to short-term results
- Clear order, structure, and rules, enabling repetition and swift onboarding of new team members
Disadvantages of the Transactional Leadership Style:
- The sole focus on performance can be demotivating and disengaging
- Rewards have a limited impact on peoples performance; at some point, other factors start to matter more
- The strict structure hampers creativity and innovation
Read more in our detailed article on this style here: the transactional leadership style.
10. Laissez-Faire Leadership Style
Sometimes a leader needs to back off a bit and let employees handle things on their own. That is not laissez-faire; that is just empowering others. Just because you avoid micromanaging, it does not mean you are a laissez-faire leader. Do avoid the laissez-faire leadership style and bear in mind that it is sometimes referred to as “the absence of leadership”.
What is the Laissez-Faire Leadership Style?
Laissez-faire leadership is a hands-off leadership style where team members are free to make all decisions. Laissez-faire leadership leads to low productivity and a perception of a disengaged leader. Laissez-faire leadership can work with highly skilled, capable, and self-motivated teams.
Laissez-Faire is the opposite of autocratic leadership and was first defined by Kurt Lewin and his colleagues in the late 1930s. Laissez-faire leadership is also known as hands-off leadership, free-rein leadership, the absence of leadership, or simply zero leadership. Laissez-faire leadership also belongs to the Full Range Leadership Model, and you can see it with it sibling styles in the image above in the transformational leadership segment.
Advantages of the Laissez-Faire Leadership Style:
- A highly skilled and experienced team can do great when making all the decisions themselves
- Team members get an abundance of creative freedom
Disadvantages of the Laissez-Faire Leadership Style:
- Teams lacking the right maturity level can quickly fall apart
- The leader is seen as uncaring or absent, leading to lower engagement and motivation
- It can lead to confusion and often to drops in productivity
More information is available in our article on the Laissez-Faire Leadership style.
In the 1930s, Kurt Lewin and his colleagues performed a set of leadership experiments. These were based on a theoretical approach which is nowadays referred to as the Lewin leadership styles. The Lewin styles consist of Democratic Leadership (mentioned previously in this list as part of the Goleman styles), Laissez-Faire leadership (mentioned above as part of the Full Range Leadership Model), and Autocratic Leadership, which is the next one coming right up.

The three leadership styles of the Lewin experiments.
Please use our image, as long as your link back to this page.
11. Autocratic Leadership Style
The autocratic leader is sadly too common even these days. The Autocratic leader is the typical despotic “Boss” who has the “My way or the highway” approach. Unfortunately, the internet is flooded with articles making this style sound like a legitimate choice when nothing could be further from the truth. Good leaders are not autocratic leaders.
What is the Autocratic Leadership Style?
Autocratic leadership is when the leader holds all the decision power and rarely consults others. Autocratic leadership is unpopular, has many disadvantages, and leads to low engagement and sometimes to a toxic environment. Autocratic leadership is useful in a crisis when control and fast decisions are crucial.
Autocratic leaders have been around for a long time in the shape of tyrants, dictators, monarchs, etc.. Still, the Autocratic Leadership Style, or rather leadership behavior, is first mentioned by Kurt Lewin et al. in their 1938 leadership experiment. The autocratic style is not defined as interchangeable, i.e., a leader is either an autocratic leader, a democratic leader, or a laissez-faire leader, with no switching, no situation dependency. It is simply the personality of the leader.
Advantages of the Autocratic Leadership Style:
- High clarity on structure, roles, and expectations
- Quick decision making and improved crisis handling, with the right autocratic leader, that is
- Can lead to increased productivity in low-skilled environments, at least temporarily
Disadvantages of the Autocratic Leadership Style:
- There is a lack of empowerment in the team, which leads to low engagement and accountability
- Too strong dependency on the leader; after all, if only the leader can make decisions, not much happens without the leader’s involvement
- Intimidation, punishment, or threats are common ways of ensuring obedience. This is, of course, not sustainable and can lead to a toxic work climate
Read more in our detailed article: the Autocratic Leadership style.
Task-oriented and Relationship-oriented leadership, the two upcoming styles, are part of the Ohio State Leadership Studies framework.
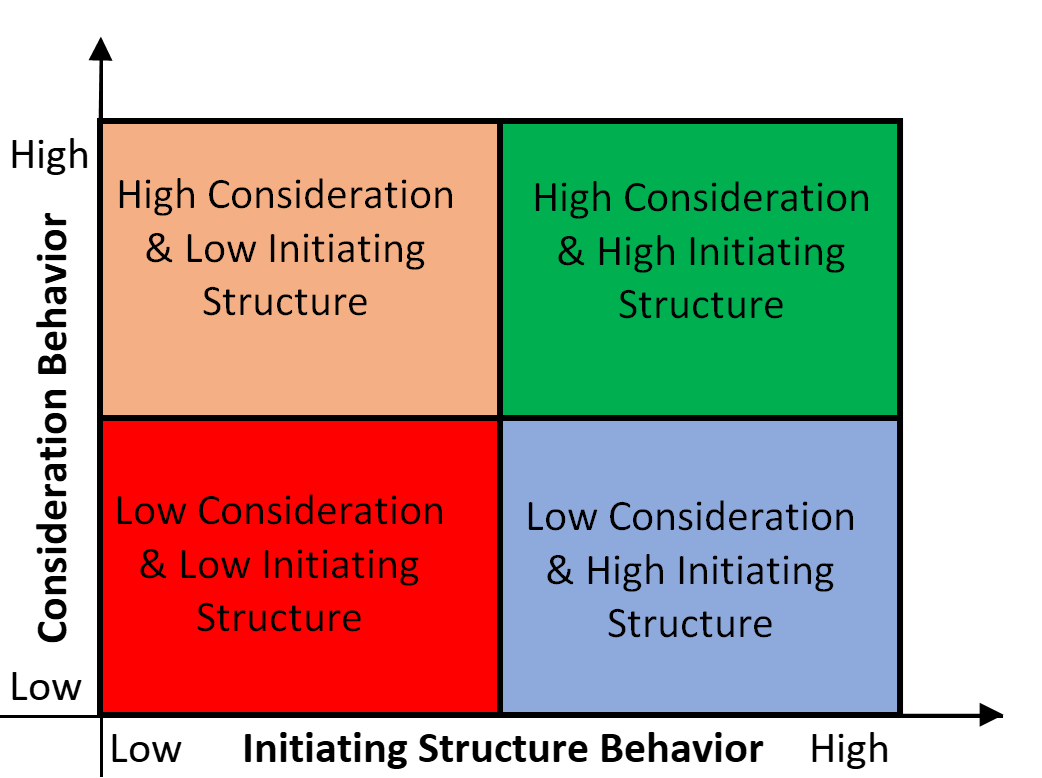
Feel free to use this image as long as you link back to this page.
12. Task-Oriented Leadership Style
Task orientation is referred to as a leadership style in some leadership models and as a leadership behavior in others.
What is the Task-Oriented Leadership Style?
The task-oriented leadership style is all about getting the job done, task execution, quality, output, and other non-human aspects. The task-oriented leader puts a second priority on relationships and people.
Task-oriented leadership is part of Fiedler’s Contingency Model of Leadership from the 1960s. It has similarities with the authority-obedience style of Blake and Mouton, the transactional leadership style from the Full Range Leadership Model, or a combination of commanding and pacesetting leadership styles from the Goleman leadership styles. In extreme cases, a task-oriented leader might even be using an autocratic leadership style, which is worth avoiding, as you know by now.
Task-Orientation is referred to as a leadership behavior under the name of Initiating Structure (Ohio State Leadership Studies) and job-oriented behavior (Michigan State Leadership Research).
Advantages of the Task-Oriented Leadership Style:
- A clear focus on production and output related parameters
- Can result in short-term productivity gains
Disadvantages of the Task-Oriented Leadership Style:
- The lack of people focus results in low engagement, motivation, and dedication of the team members
- It can go too far and lead to high amounts of stress or illness among team members
13. Relationship-Oriented Leadership Style
Relationship-Orientation is seen as a style in some models, and as a behavior in other leadership models.
What is the Relationship-Oriented Leadership Style?
A relationship-oriented leader has a strong focus on developing bonds and relationships with team members and other stakeholders. Relationship-oriented leadership leads to trust, friendship, and a supporting team climate.
Relationship-oriented leadership is one of two styles in Fiedler’s Contingency Model from the 60s, and it can be compared with transformational leadership from the Full Range Leadership Model or a mix of democratic, affiliative, visionary, and coaching leadership from the six leadership styles by Goleman. Relationship-oriented leadership can also be compared to Consideration behavior (Ohio State Leadership Studies) and employee-oriented behavior (Michigan State Leadership Research).
Advantages of the Relationship-Oriented Leadership Style:
- People focus builds engagement, unity, and loyalty
- Develops people in the long-term and allows for creativity and innovation
Disadvantages of the Relationship-Oriented Leadership Style:
- Can result in a lack of performance
- Less clarity in what to do, and when and how it should be done
The following four leadership styles: Telling, Selling, Participating, and Delegating leadership belongs to the Situational Leadership Model from the 1980s.
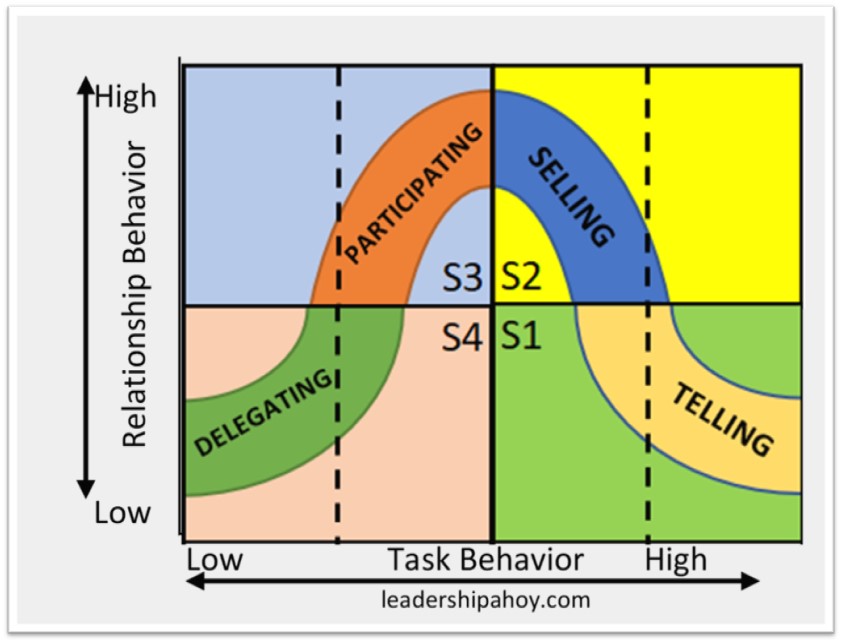
If you use the image above, please link back to this page.
14. Telling Leadership Style
The telling leadership style, also known as the directive or guiding leadership style, is specifically intended for inexperienced and immature teams.
What is the Telling Leadership Style?
The telling leadership style is when the leader tells team members what to do and when to do it. Telling leadership is intended as an early step in the development of a team, and it should be done in a guiding way so that the team members can actively learn from the leader, making telling leadership superfluous in the near future.
Telling leadership, also referred to as directing or guiding leadership, comes from the Situational Leadership Model and is its most task-oriented style. As the team learns and grows, the leader moves on to more empowering leadership styles.
Telling leadership is similar to directive/commanding leadership when it comes to detailed instructions, the decisions being made by the leader, and the style being applied on a temporary basis. Telling leadership is very different from autocratic leadership since it is intended to be used in the early development of a team and then be replaced by other styles, an ambition the autocratic leadership style completely lacks.
Advantages of the Telling Leadership Style:
- High clarity in structure, tasks, processes, and instructions
- Low skilled teams can become productive while also learning from the leader
Disadvantages of the Telling Leadership Style:
- There is little participation and engagement on the part of the team members
- It rests entirely on the knowledge of the leader, which must be skilled and experienced in all the team members’ roles
15. Selling Leadership Style
Selling leadership is pretty much what it sounds like: the leader sells the team members on a direction, idea, decision, or something else.
What is the Selling Leadership Style?
Selling Leadership is when a leader decides what, when, and how to do things, but convinces and inspires the team to perform by explaining the underlying purpose. A selling leader tries to build commitment and interest and let the team members influence who should be involved in executing the decision.
The Selling leadership style, also known as coaching or explaining leadership, is the second phase approach in the Situational Leadership Model by Hershey and Blanchard. After the leader has gone through the first maturity stage with the team, where telling leadership is needed, it is time for Selling leadership. The selling leader builds more engagement and continues to provide learning opportunities for the team by involving them in why decisions are taken and let them participate in shaping the execution. Selling leadership is difficult to compare to the other styles, but perhaps it would correspond to a significant portion of commanding leadership with some additions of pacesetting, visionary, and coaching leadership.
Advantages of the Selling Leadership Style:
- Fast decisions with slightly more engagement
- Facilitates learning in an inexperienced team
Disadvantages of the Selling Leadership Style:
- Still lacking full engagement
- It takes more time than directive styles
16. Participating Leadership Style
Participating leadership is used in the third maturity phase of the Situational leadership model, going from selling leadership to a new and more participative level.
What is the Participating Leadership Style?
Participating leadership focuses more on people and alignment rather than giving detailed instructions to them. The team members are mature enough to execute tasks but still need the leader to drive purpose, engagement, and vision to provide alignment and context.
Participating leadership is sometimes called facilitating, or collaborative leadership and it is the third style in the Situational Leadership model. Having passed through the telling and selling leadership situations, the team is now experienced and skilled enough to handle the execution as well. The leader is still needed to provide overall context and motivation. Participating leadership might seem closely related to democratic leadership, but I think coaching and visionary leadership is even more comparable. It would not be a stretch to say that participating leadership also resembles portions of transformational leadership.
Advantages of the Participating Leadership Style:
- Team members are empowered to handle operational tasks
- It provides alignment and collaboration between team members through facilitation and coaching
Disadvantages of the Participating Leadership Style:
- Collaboration can be time-consuming
- It can lack in performance
Participating leadership is very similar to democratic leadership mentioned further above. It takes a lot of skill to properly balance this style so you get the engagement, creativity and collaboration, without going too far and resulting in long meetings about every decision, causing delays and reduced performance. I teach you exactly how to do this in our democratic leadership course where I walk you through the techniques I have used to transform teams of more than a thousand people to great success.
17. Delegating Leadership Style
The pinnacle of the situational leadership model, delegating leadership, is a sign of a mature, experienced, and skilled team. If it works properly, that is.
What is the Delegating Leadership Style?
Delegating Leadership is when a leader of a mature and experienced team focuses on building higher empowerment and autonomy in the team. The leader stands back and gets involved if the team members need it, but not for leader-initiated monitoring purposes.
The Delegating Leadership style is the most evolved style in the Situational Leadership model. It is the last phase in developing the team, and it compares well to a Transformational or Visionary leadership style where the leader can genuinely focus on the overarching topics rather than operational issues.
Advantages of the Delegating Leadership Style:
- Combines strong performance with lots of focus on people
- It is highly empowering, engaging, and effective
Disadvantages of the Delegating Leadership Style:
- Only works in highly experienced and skilled teams
- It takes time to implement and can lead to bad results if implemented in the wrong situation
The following three styles, bureaucratic, charismatic, and traditional leadership styles belong tI have o the framework of Max Weber, which originated in the 1920s.
18. Bureaucratic leadership Style
Bureaucratic leadership was called rational-legal leadership at its inception. Rational principles built on laws, rules, and regulations are the foundation of bureaucracies. In turn, bureaucracies themselves have enabled central governing and larger national agencies, a cornerstone of building society.
What is the Bureaucratic Leadership Style?
Bureaucratic leadership is characterized by rigid rules, high standardization, and stiff division of labor. Bureaucratic leadership works best in organizations where regulations and standards are of great importance. Bureaucratic leadership hampers change, creativity, competition, and development.
Bureaucratic leadership, or as rational-legal leadership as it was called back then, was one of the three types of authority defined by Max Weber in the 1920s. The other two were traditional leadership and charismatic leadership.
Advantages of the Bureaucratic Leadership Style:
- Clear definition of roles, expectations, processes, and tasks
- Enables adherence to strict rules, allowing objective judgment
- Drives efficiency through specialization and transaction volume
Disadvantages of the Bureaucratic Leadership Style:
- The reliance on rules limits creativity and innovation
- Slow and poor adaptation to change due to structural rigidness
- Competition and collaboration suffers due to the high specialization and silo structure
Read more in our detailed article: the Bureaucratic Leadership style.
19. Charismatic Leadership Style
The Charismatic Leadership Style is not just about being charismatic as a person and a leader, it is all about charisma and not much else.
What is the Charismatic Leadership Style?
Charismatic leadership is based on the leader's personal charisma to a very high degree. Charismatic leadership can be very inspirational and motivational, leading to unity and engagement. Charismatic leaders risk becoming autocratic one-man shows, which can lead to manipulation, bad deeds, and disasters.
Charismatic leadership forms the three types of authorities, as defined by Max Weber in the 1930s, together with traditional and bureaucratic leadership.
Advantages of the Charismatic Leadership Style:
- Inspirational and unifying
- Builds strong commitment and purpose among the followers
- Can help deliver a long term plan, or even a “cause”
Disadvantages of the Charismatic Leadership Style:
- The complete dependency on the personal characteristics of the leader, making succession planning difficult
- Risks becoming a cult where the leader stands above everyone else, perhaps even above society and laws
- The high expectance on obedience limits transparency, creativity, and innovation
Read more in our subject article: the Charismatic Leadership style.
20. The Traditional Leadership Style
This old approach to leadership is what the kings and queens of history relied upon. However, given its foundation, it is debatable whether it belongs on this list of leadership styles at all.
What is the Traditional Leadership Style?
Traditional Leadership is when established tradition, culture, and order, give a leader the authority to rule. Traditional Leadership mainly builds on autocratic or paternalistic principles, giving the leader absolute powers. Kings, Queens, Princes, Chiefs, and Elders are examples of Traditional Leaders.
The traditional leadership style is part of the three types of authorities defined in Max Weber’s book “Classification of Authorities” of 1932. Traditional leadership has many similarities with autocratic leadership; the main difference is that the traditional leader has more substantial legitimacy. Nevertheless, the pros and cons are similar between the two styles.
Advantages of the Traditional Leadership Style:
- Empires were built through the use of traditional leadership
- Quick decision making, just like the autocratic leadership style
- The leader’s authority is complete, and orders are followed
Disadvantages of the Traditional Leadership Style:
- The leader is selected out of tradition rather than capabilities, performance, and passion
- The autocratic part leads to low performance, low engagement, and even a toxic climate
21. Paternalistic Leadership Style
The paternalistic leadership style is one of the oldest styles in human history. It was all that mattered back in the days of troglodytes and dangerous predators.
What is the Paternalistic Leadership Style?
Paternalistic leadership is when an autocratic leader makes all the decisions for the good of the group. A paternalistic leader has the best intentions for the followers, and act as a parental figure with high authority, even if they are left out of the decision-making.
Paternalistic leadership is as old as humanity with the village elder, alpha leader, top caveman acting as the pack leader, and in most cases, it was a male. Good paternalistic leaders ensured group survival, with all that entailed in terms of food, shelter, reproduction, and defense. Some theories see paternalistic leadership as a specific type of autocratic or authoritarian leadership, rather than a distinct leadership style of its own. Paternalistic leadership is used in some parts of the world but is relatively uncommon in the west.
Advantages of the Paternalistic Leadership Style:
- Quick decision making and fast execution
- Genuine care for the followers can build engagement and empowerment, despite the autocratic streaks
Disadvantages of the Paternalistic Leadership Style:
- Succession planning can be difficult
- The leader becomes a bottleneck since all decisions need to flow through one person
- A paternalistic leader with bad intentions can cause severe damage
22. Spiritual Leadership Style
The Spiritual Leadership Style truly sticks out among other leadership styles with its heightened focus on well-being, the mind, and perhaps even the soul.
What is the Spiritual Leadership Style?
Spiritual leadership is when workplace spirituality is at the top of the agenda, specifically focusing on vision, hope or faith, and altruistic love. In addition, spiritual leadership involves developing the inner lives of team members and achieving meaningful objectives as an organization.
Louis Fry developed spiritual leadership in the early 2000s as part of the intrinsic leadership theory. The need for spiritual leadership increases due to global challenges, and employees that look for more meaningful occupations.
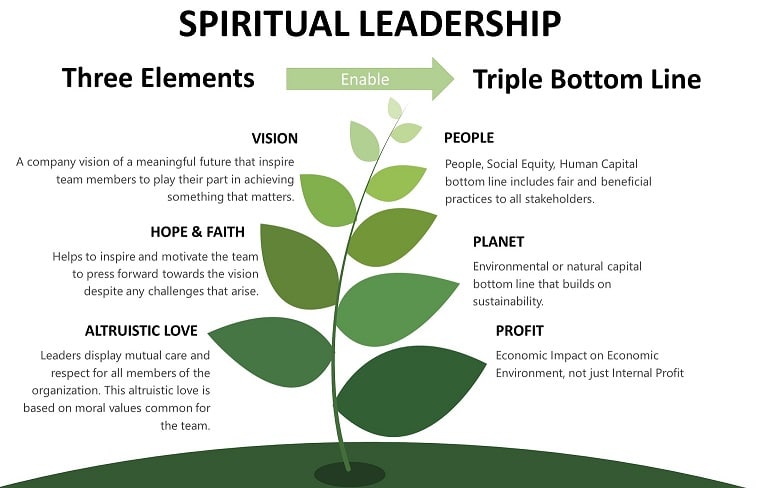
Feel free to use the image as long as you link back to this page.
Advantages of the Spiritual Leadership Style:
- It can provide a strong sense of belonging
- Corporate Social Responsibility is often a cornerstone
Disadvantages of the Spiritual Leadership Style:
- Non-spiritual people might not fit in
- It can lead to a too nice of an environment and losing sight of business objectives
For more information, refer to our in-depth article on the spiritual leadership style.
The following five styles belong to the Blake and Mouton Managerial Grid framework: Impoverished, Country-Club, Authority-Obedience, Team, and Middle-of-the-Road leadership.
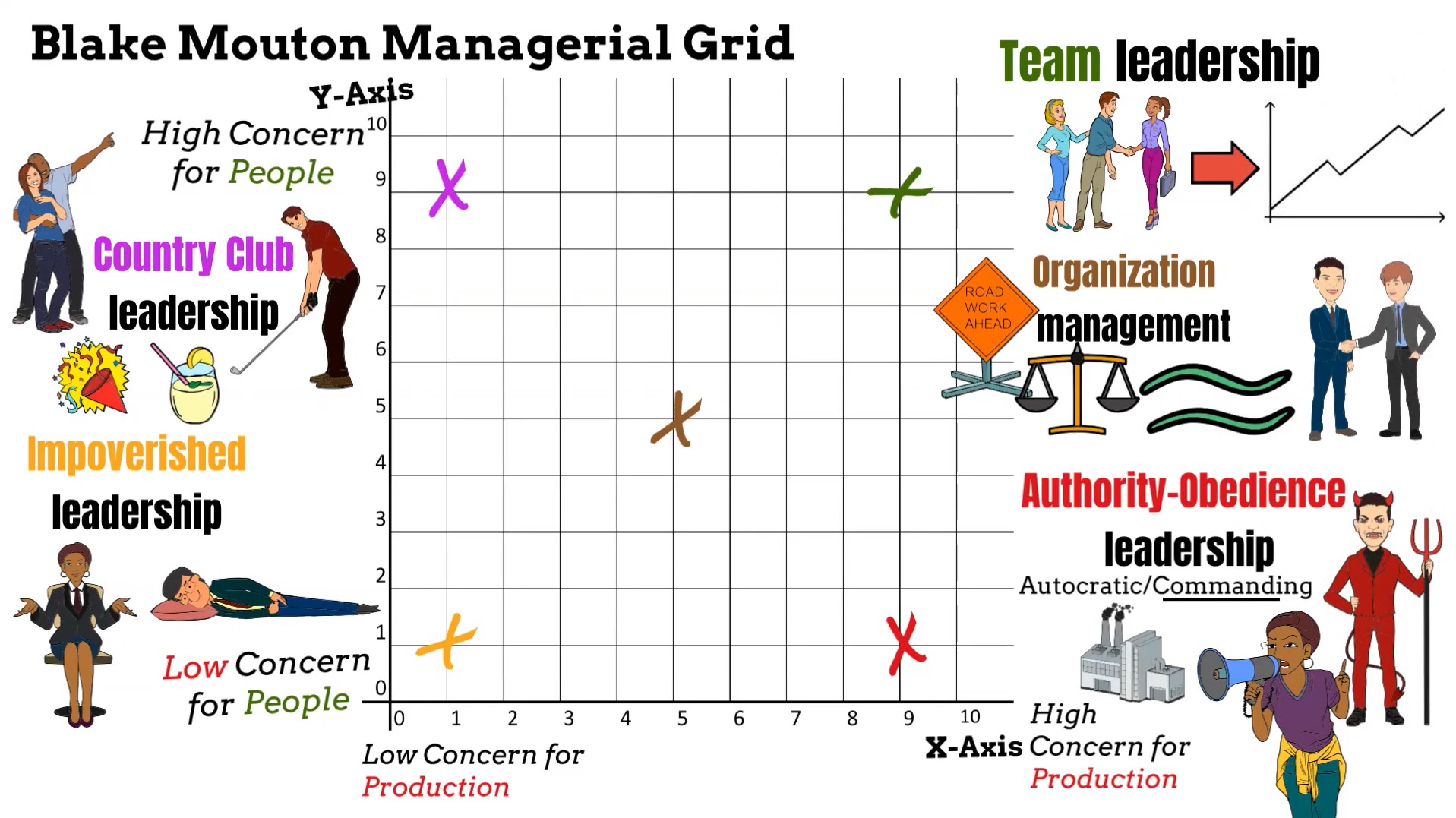
Feel free to use this image as long as you link back to this page.
23. Impoverished Leadership Style
I hope that very few leaders aim to use the impoverished leadership style on purpose. No sane leader would, and the name of the style itself implies that it should be avoided.
What is the Impoverished Leadership Style?
Impoverished Leadership is when a leader shows little concern for people and production, indicating low interest in both relationships and performance. In impoverished leadership, the followers don’t care enough even to try to perform since the leader shows no interest in the team or organization.
The Impoverished leadership style originates from the Blake and Mouton managerial grid from the 1960s and can be seen as a bad case of Laissez-faire leadership, which is a somewhat comparable style present in several other models.
Advantages of Impoverished Leadership
There are no pros of Impoverished leadership. Removing a leader using this style would lead to better results than if the leader remains.
Disadvantages of Impoverished Leadership
- The absence of concern for people leads to low engagement and high turnover
- The absence of concern for production leads to a lack of performance
Additional information can be found in our article on the Impoverished Leadership style.
24. Country Club Leadership Style
The Country Club leadership style must be the style with the loveliest name of them all. This style is sweet, but sadly, it is not sustainable due to its low performance.
What is Country Club Leadership?
Country club leadership is when a leader focuses too much on the employees, combined with a severe lack of concern for performance and output. The Country Club leader ensures a friendly environment, with low expectations of people. As a result, employees enjoy themselves but get little done in terms of performance.
The Country Club leadership style originates from the Blake and Mouton managerial grid leadership styles which were created in the 1960s. The overly strong focus on people and the lack of focus on production can be compared to an extreme version of affiliative leadership to connect to more modern leadership styles.
Advantages of Country Club leadership:
- Friendly and harmonious team environment
- Low staff turnover
- Very little anger, stress, and conflict
Disadvantages of Country Club leadership:
- Little to no performance
- The lack of output risks the existence of the organization or business
Read more about it on our site right here: the Country Club Leadership style.
25. Authority-Obedience Leadership Style
Authority-Obedience leadership is also referred to as Produce or Perish leadership, which is more descriptive of what this leadership style is about.
What is the Authority-Obedience Leadership Style?
Authority-obedience leadership puts a very high focus on production with little to no concern for the involved people. A leader that uses Authority-Obedience leadership gives orders and directs people to execute them without emotion since performance is the only thing that matters.
Authority-obedience leadership, or Produce and Perish leadership, is part of the five styles included in the Blake and Mouton managerial grid which was created in the 1960s. The strong autocratic direction makes it comparable to autocratic leadership, which is one of the Kurt Lewin behavioral leadership styles or the more modern and situational style of Commanding/Directive leadership or the performance-focused pacesetting leadership.
Advantages of Authority-Obedience leadership:
- High production output
- Quick decisions since the leader makes all the decisions
- High clarity of expectations, jobs, and tasks
Disadvantages of Authority-Obedience leadership:
- High turnover due to the lack of people focus
- The lower levels of initiative, creativity, and engagement among employees
- If used for a long time, productivity will suffer due to the two disadvantages above
Read more in our detailed article on the Authority-Obedience Leadership style.
26. Middle-of-the-Road Leadership Style
The Middle-of-the-Road leadership style is a compromise of focus on production versus people, which is also known as organizational leadership.
What is the Middle-of-the-Road Leadership Style?
Middle-of-the-road leadership includes a medium focus on both people and production, respectively. A Middle-of-the-Road leader balances performance with consideration for employees. The compromise of Middle-of-the-Road leadership ensures a good work environment but provides less than maximum output.
Middle-of-the-Road leadership, or organizational leadership, stems from the Blake and Mouton managerial grid theory of the 1960s. There is no good comparison to a single modern style since the compromise is created by the appropriate use of several different leadership styles. Suppose you have a good mix of democratic leadership and affiliative leadership from the six leadership styles by Goleman. In that case, you might reach a similar result as with the Middle-of-the-Road leadership style.
Advantages of Middle-of-the-Road leadership:
- The balanced approach is better than the extremes of Authority-Obedience, Country Club, or Impoverished styles
- It is sustainable in the longer term
Disadvantages of Middle-of-the-Road leadership:
- Great performance is highly unlikely
- A compromise approach can be problematic in extreme situations that call for a complete focus on people or production, even temporarily
27. Team Leadership Style
This is the best of the five leadership styles of the Blake and Mouton managerial grid theory as it combines great care for people with strong performance.
What is the Team Leadership Style?
Team Leadership is when the leader shows a high level of concern for both people and production. Team Leadership is a very effective leadership style and leads to great performance goals and fantastic employee engagement and well-being. However, it is difficult and time-consuming to implement Team Leadership.
The Team leadership style is the best pick from the Blake and Mouton managerial grid which was created in the 1960s. This is the only style in the managerial grid that reaches high performance and high people engagement and involvement at the same time. Team leadership can be seen as an optimum mix of the Goleman leadership styles, since that should have the same result of strong output with a retained focus on people.
Advantages of the Team Leadership Style:
- Strong engagement leads to creativity, innovation, and collaboration
- Strong output and performance
- Robust and sustainable from a performance as well as a people perspective
Disadvantages of the Team Leadership Style:
- Very difficult to reach, perhaps impossible for some leaders and teams
- Time-consuming and investment heavy
- Requires an exceptionally skilled leader as well as the right team members
Leadership Styles Sources
(Join our newsletter and get some of my secret tips for each of the Goleman leadership styles.)
“A Handbook of Leadership Styles”, Demirtas and Karaca, Cambridge Scholars Publishing.
https://online.campbellsville.edu/business/delegating-leadership-style/https://online.stu.edu/articles/education/what-is-situational-leadership.aspx
https://wellbeing.gmu.edu/articles/11237
https://hbr.org/2002/10/the-leadership-journey
http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.983.5330&rep=rep1&type=pdf
https://www.psychologytoday.com/sg/blog/cutting-edge-leadership/201210/what-is-charisma-and-charismatic-leadership
Robert J House, “A 1976 Theory of Charismatic Leadership”: https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED133827.pdf
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/320283218_Laissez-Faire_leaders_and_organizations_how_does_Laissez-Faire_leader_erode_the_trust_in_organizations
https://cals.arizona.edu/classes/aed301/laissez
https://publichealth.berkeley.edu/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/CPHPL__Leadership_That_Gets_Results.pdf
https://home.ubalt.edu/tmitch/642/E%20articles/house%201996%20path%20goal%20reformulaton.htm
http://www.academia.edu/download/33585213/HBR_MustReads_Managing_People.pdf#page=4
https://www.forbes.com/sites/mikemyatt/2012/01/12/businesses-dont-fail-leaders-do/#3e0f9d6c97a4
http://mchnutritionpartners.ucla.edu/sites/default/files/images/HBRLeadershipGetsResults1.pdf
Refer to the respective in-depth articles for additional sources.