The Trait Theory of Leadership focused on leadership studies in the first half of the 20th century before behavioral and contingency theories started gaining ground. This article explains the trait theory of leadership, its origins, and several trait theory examples, guiding us toward developing exemplary leadership traits. Many of them are skills and characteristics I aim to improve to increase performance in my roles as a CEO.
What is the trait theory of leadership?
The trait theory of leadership analyzes traits such as mental, physical, and social characteristics of leaders. The trait theory of leadership argues that leaders can become more successful by developing and learning those key traits, a significant difference from the earlier Great Man Theory.
When talking about Alexander the Great, Napoleon Bonaparte, Mahatma Gandhi, Nelson Mandela, John F Kennedy, Margaret Thatcher, etc., the first thing people think about is leadership. All these persons (and not only they) have had millions of followers that believed everything they do is right. But why were they the ones that changed the world? How did they reach such heights? What made them so famous? These are not new questions. People have been looking for answers for centuries. There have been myriads of theories trying to explain what traits leaders have or should have. One of such approaches is known as the trait theory of leadership.
Everything began in the 1800s when several research studies emerged trying to respond to the so-called Great Man theory of leadership. The latter was initially proposed by Thomas Carlyle [1], who was sure leaders are born with concrete traits, which can't be acquired over time.
However, the Great Man theory cannot answer a list of questions such as "what about people who have supposed leader traits but are not leaders?" or "what about the leaders who don't possess those traits but still succeed in leadership and management?" [3] In this regard, Ronald Reagan's words sound quite appropriate:
"The greatest leader is not one who does greatest things. He is the one that gets the people to do the greatest things." [2]
What is the main idea of the trait theory?
The main idea of the trait theory of leadership is that some specific traits are seen in most leaders. Trait theory research aims at analyzing mental, physical, and social characteristics in an attempt to understand what combination of characteristics is common among successful leaders.
Before you continue, consider getting our leadership theories e-book called Leadership Origins, which contains in-depth information on ten impactful and well renowned leadership theories, including Trait Theory. Great reference material for students, and an awesome learning experience for managers and aspiring leaders.
Develop yourself with these products from Leadershipahoy.com
The Characteristics of Trait Theory of Leadership
Unlike the Great Man theory, the trait theory of leadership doesn't believe good leaders are born with specific traits. Instead, the theory focuses on characteristics that make persons good leaders. So if working on them, anyone can become a leader with many followers. Gordon Allport was the first investigator who thought there are traits anyone can develop to become a good leader. Shortly, many others welcomed his idea - Raymond Cattell, B.F. Skinner, and Ralph Stogdill. Allport is known for identifying up to 18,000 words in the English-language dictionary that describe a good leader. Those words were divided into three groups of cardinal, central, and secondary traits and skills. There were many questions regarding the validity of this theory, but it was a solid move to a new thesis.
According to the trait theory of leadership and its advocates, leaders are better at showing themselves off, are psychologically better adjusted to display better judgment, engage themselves in social activities, always know more, and never hesitate to take the lead. In other words, people who want to become good leaders should always learn, be informed, know how to display themselves and appear in situations where these traits could be helpful. In this sense, any of the aforementioned characteristics can be developed over time according to the trait theory of leadership.
However, if Allport divides the leader traits into three groups, Henry Fayol thought there are additional characteristics groups, such as physical, mental, moral, educational, technical, and experience. Another researcher, Charles Brid, pointed to twenty lists of traits attributed to leaders.
Logically, all researchers take a set of traits that they think are common for leaders. Ralph M. Stogdill tried to collect them into one place. [4]
Trait Theory of Leadership Examples
Stogdill's study shows that traits of successful leaders include:
- Physical and constitutional factors: Among them, we can mention height, weight, physique, health, and appearance. Scientists think they have a certain impact on a person's success, and activity, in general. (But if Alexander the Great is said to be extremely handsome with "a certain melting look in his eye", the same can't be said about Napoleon Bonaparte, who had the appearance of being shorter than he really was. [6])
- Intelligence: This is the most important trait, as leaders generally have a higher level of intelligence than the average of their followers. It is described as an ability to think scientifically, analyze accurately and interpret problems. It's a natural quality related to the human brain and its activity. But psychologists think it can be improved with the help of proper training programs. Due to such an ability, good leaders make decisions that move the group forward.
- Self-confidence: As great leaders are self-assured, their followers act in the same way. At least, they are sure of what they are doing or believing.
- Decisiveness: Great leaders know that they are the ones expected to make the tough decisions, and they are confident in making those choices.
- Emotional Stability: Successful leaders are consistent in their actions; know how to control their emotions, especially anger. Avoiding overreactions is what every leader needs. (Learn more in my book about your inner dialogue and how to harness it. Available at Amazon: Intrapersonal Communication. (Ad))
- Adaptability and flexibility: You cannot find a leader that does not think outside of the box. Such an ability helps them adapt quickly to changing situations.
- Courage and responsibility: Good leaders never hide from challenges. In addition, they take on responsibility (and take ownership of their mistakes).
- Art of Communication: Great leaders know various techniques of interacting with both other leaders and team members.
- Role model: Leaders are skilled. Therefore, team members always know whom they will look at when unaware of how things should be done. In this sense, leaders should have some technical skills of planning, delegation, analysis, making decisions, controlling, etc.
- Trustworthiness: Team members always trust them. For this, leaders should have the ability to work with team members by winning their confidence and loyalty. As a result, people will cooperate with them willingly and not under pressure.
- Vision and Foresight: Successful leaders can foresee the future, visualize trends and act according to them.
- Empathy: Leaders ought to be able to observe things or situations from the point of view of others. This ability helps leaders predict and understand the behavior of people.
- Motivation: Leaders should be great motivators. They know how to inspire team members to do their best.
However, all these traits are only suggestive and the list is not exhaustive. This means that a person may not have most of them but still be a successful leader. Vice versa, a person might have all the aforementioned qualities but fail when it comes to leadership. Anyway, according to the trait theory of leadership, these qualities appear in most leaders. So when thinking of traits that leaders should have, this list is what describes most of them.
Many different lists of leadership traits have emerged over the years[8}. In the earlier years, six to eight traits were seen as the common leadership traits, only to be reduced to three or four traits in the 1980s. Later studies, in 2004, resulted in a long list of fourteen different leadership traits. Here are a few examples in chronological order.
In 1948, Stogdill concluded the following list of leadership traits:
- Intelligence
- Insight
- Self-confidence
- Alertness
- Responsibility
- Initiative
- Persistence
- Sociability
Retaining some similarities with Stogdill's list, here is Mann's list of leadership traits from 1959:
- Intelligence
- Masculinity
- Adjustment
- Dominance
- Extraversion
- Conservatism
Here is an example of a shorter list. McCall and Lombardo concluded the following list of leadership traits in 1983:
- Emotional Stability and Composure
- Admitting error
- Good Interpersonal Skills
- Intellectual breadth
Let us end with a more modern take on the topic. Zaccaro, Kemp, and Bader concluded the following list of leadership traits in 2004:
- Extraversion
- Agreeableness
- Conscientiousness
- Openness
- Neuroticism
- Honesty and Integrity
- Charisma
- Intelligence
- Creativity
- Achievement motivation
- Need for Power
- Oral and Written Communication
- Interpersonal Skills
- General Problem-Solving
Traits concerning interpersonal skills, communication, integrity, and extraversion seem to become more common in the later lists, especially during and after the 80s. I think this is also a sign of leadership changing over the years and adapting more to leading knowledge workers, rather than the old school Taylorism approach to humans as cogs in the machinery. We offer guides, books, courses, and coaching to help you develop your leadership and traits further. Please have a look at our products and services page.
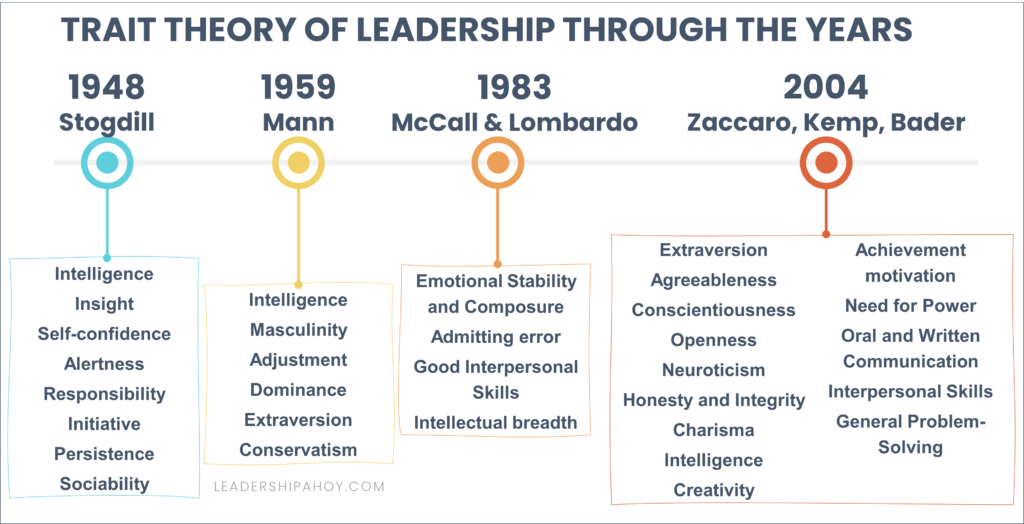
Trait theory of leadership through the years. (Feel free to use the image as long as you link back to this page.)
Trait Theory of Leadership Advantages and Disadvantages
The biggest advantage of the trait theory of leadership is that it moved away from the old Great Man theory that had no serious scientific background. All researchers were trying to find a correlation between successful leaders and a limited number of factors describing them. But Carlyle showed that leaders have traits not included in the factors list. Therefore, the Great Man theory can't be treated as a reliable approach.
Nevertheless, the trait theory of leadership is one of the major theoretical areas in studying human personality. It tries to find differences between individuals. In addition, it was one of the first systematic attempts to study leadership and understand its nature. At the core, this approach believes that various traits form a personality and tries to measure it somehow. So knowing those traits and dispositions, anyone who wants to become a successful leader can improve them.
"Leadership consists not in degrees of technique but traits of character; it requires moral rather than athletic or intellectual effort, and it imposes on both leader and follower alike the burdens of self-restraint." - Lewis H. Lapham [7]
On the other hand, the trait theory of leadership received a massive dose of criticism as well. Honestly, the accusations were quite reasonable. The theory is straightforward, but it still fails to produce clear-cut results. In this regard, Jenning's words fully describe the theory: "Fifty years of study have failed to produce a one Personality trail or set qualities that can be used to discriminate leaders and non-leaders". [5]
Develop yourself with these products from Leadershipahoy.com
The Advantages of the Trait Theory of Leadership
- Trait Theory helped to move the focus from the Great Man Theory of Leadership, opening up new possibilities in the leadership studies field.
- It brought significant advances in studying human personalities and characteristics.
- The theory brings well-needed complexity to leadership, rather than reducing it two just a few behavioral leadership styles as in the Lewin leadership studies.
- It guides leaders on which types of characteristics to improve further
The Disadvantages of the Trait Theory of Leadership
Here are some of the weaknesses, disadvantages, and limitations of the trait theory of leadership:
- The trait theory of leadership fails to cover all situations and circumstances.
- Various authors suggest different lists of traits, making the theory less specific
- Trait theory does not consider other leadership factors.
- Trait theory doesn't provide any comparative results.
- No surveys show how different degrees of the same trait affect the leader's behavior and performance.
- In the end, there are no definite tests for the measurement of these traits.
Further Reading
Before you continue, consider getting our leadership theories e-book called Leadership Origins, which contains in-depth information on ten impactful and well-renowned leadership theories, including Trait Theory. Great reference material for students, and an awesome learning experience for managers and aspiring leaders.
I recommend you read our articles on the Ohio State and Michigan University studies on leadership, which involve behavioral leadership approaches during the 1940s and 50s. Once the contingency theories of leadership emerged in the 1960s, such as Fiedler's Contingency Theory of Management, most approaches to leadership include situational elements. You can read about these theories and more modern leadership approaches such as the Situational Leadership Model, transformational, servant, and adaptive leadership in our leadership styles portal, which might be the biggest leadership styles database available online. If you are sincere about improving your leadership capabilities, I also suggest you read our article on how to create a leadership development plan for yourself. For a general article, consider 12 common leadership styles and how to choose yours.
Sources
[1] Thomas Carlyle, "The Hero as Divinity" in Heroes and Hero-Worship (1840).
[2] https://www.leadershipnow.com/leadingblog/2011/02/ronald_reagan_on_leadership.html
[3] http://www.jiwaji.edu/pdf/ecourse/political_science/MA_POL.SC._IV_401_LEADERSHIP_THEORY.pdf
[4] Stogdill, Ralph M. Personal Factors Associated With Leadership: A Survey Of The Literature. The Journal of Psychology 25.1 (1948)
[5] https://www.yourarticlelibrary.com/leadership/trait-approach-to-leadership-its-criticism-explained/64004
[6] https://www.britannica.com/story/was-napoleon-short
[7] https://www.brainyquote.com/quotes/lewis_h_lapham_166526#
[8] https://www.technofunc.com/index.php/leadership-skills-2/leadership-theories/item/trait-theory-of-leadership-2




